Business process management (BPM)
What is BPM?
Business process management (BPM) is a methodology to manage processes and workflows in an organization. The goal of BPM is to increase efficiency, performance, and agility in the day-to-day operations of a business. BPM has been widely adopted by organizations and is essential for any enterprise businesses that want to be competitive in today’s marketplace.
Watch this video to learn about Pega’s case management software and how it can empower your organization to efficiently manage complex business processes.
Why use BPM?
BPM helps simplify and automate operations so you can reduce costs and improve business agility. By using BPM, organizations create repeatable solutions that can be efficiently reused and tailored to meet the requirements of diverse users, product lines, channels, and geographies.
Benefits of business process management
Business process management (BPM) drives efficiency in several ways:
- Cost reduction and operational agility: BPM simplifies and automates operations, unlocking avenues for substantial cost cuts.
- Repeatable solutions: Using BPM helps create efficient, scalable, and adaptable solutions.
- Streamlined workflows: BPM identifies and optimizes processes, reducing redundancies and removing bottlenecks.
- Enhanced user experience: BPM eliminates bottlenecks, reduces tedious tasks, and improves accuracy, which translates to fewer mistakes and a better overall experience for customers and employees.
- Structured service delivery: BPM creates a structured environment, reducing response times and enabling faster customer service.
It’s more than just operational enhancements. BPM shapes a responsive, cost-effective, and user-friendly organizational landscape. By integrating BPM, you can position yourself to thrive in an ever-evolving marketplace.

How does BPM work?
BPM uses a combination of technologies – including workflow automation, AI-powered decisioning, and case management – to build comprehensive solutions for organizations. By leveraging these technologies, organizations improve business processes that enable them to bring products to market faster; make, market, and sell more profitably; and deliver superior customer service.
Relationship between BPM and automation
BPM and business process automation (BPA) form a symbiotic relationship at the heart of efficient organizations. Together, they create a dynamic synergy, streamlining operations, reducing errors, and enhancing overall performance. To break down the distinctions between BPM and BPA:
BPM
- Overarching strategy
- Defines, models, and optimizes business processes
- Identifies areas in a workflow that can benefit from automation
BPA
- Execution arm of BPM
- Utilizes technology to automate processes
- Actualizes BPM's identified enhancements
- Ensures that routine, rule-based tasks are executed seamlessly, freeing up human resources for more strategic, creative, and complex endeavors
Industry case studies
Learn how Cisco is succeeding at digital transformation by embracing BPM.
See how Banco Santander Basil transformed client services with BPM.
Learn how Highmark Health uses a BPM approach to create innovative solutions.
Different types of BPM
There are many flavors of BPM, each catering to specific organizational demands:
Integration-centric BPM
Integration-centric BPM targets processes with minimal human involvement, relying on APIs for efficient data integration, as seen in HRM or CRM systems.
Human-centric BPM
Human-centric BPM focuses on processes requiring human interaction and approvals, offering intuitive interfaces for task assignments and accountability.
Document-centric BPM
Document-centric BPM addresses documentation processes. From creation and review to approval and storage, BPM streamlines everything involved with business-critical documents, which makes it easier to accomplish tasks such as formalizing intricate contracts or ensuring data privacy.

Pega is named a Leader in The Forrester Wave: Task-Centric Automation Software, Q4 2024 report.
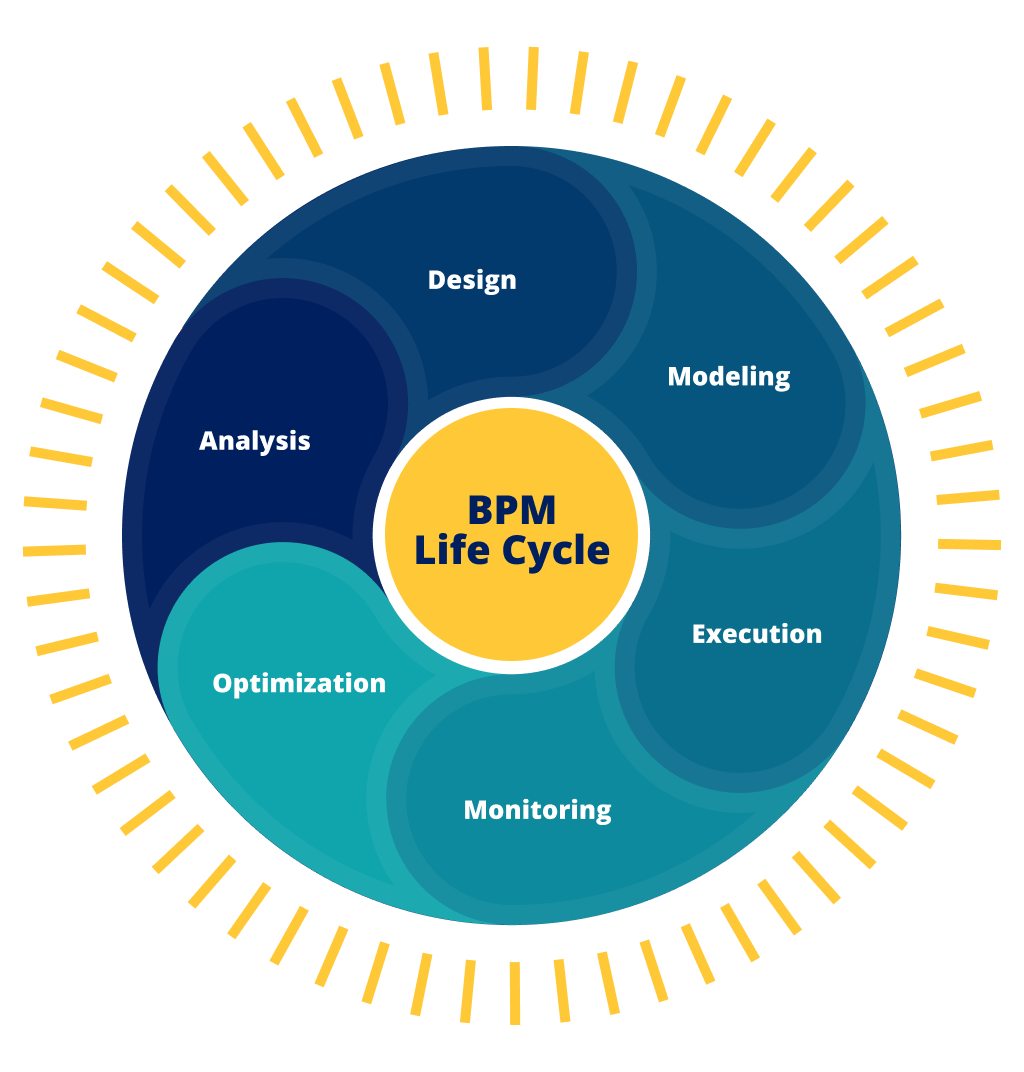
BPM Lifecycle
- Analysis
Discover and identify processes and workflows that can be created or optimized to meet business requirements or improve performance. - Design
Create process designs that include human-to-human, system-to-system, or human-to-system interactions. Designs should aim to reduce errors and maintain relevant operating procedures or SLAs. - Modeling
Use software tools to effectively model and evaluate process designs. Once a process design is ready, use varying input values to observe its behavior. If undesirable behavior is observed, make design changes iteratively. - Execution
Automate processes with business rules, decisioning, case management, and other related technologies. - Monitoring
Leverage reporting data collected from processes for performance, errors, and compliance. Monitoring allows businesses to evaluate executed BPM solutions against corresponding design models and relevant KPIs. - Optimization
Leverage data from the modeling and monitoring phases to identify areas of the solution that can be improved to derive higher efficiency and better value.
What’s included in BPM?
Turns intelligence into action by tapping into data, analyzing the current need, and providing the best response at that moment.
Uses AI to predict customer needs, personalize interactions, and streamline experiences across channels.
Manages complex human and machine work from start to finish with a case used as the epicenter to manage tasks and outcomes.
Automates complicated processes. Setting rules puts goals into action within a business application.
Makes statistics available that you can analyze in comprehensible reports to improve your business.
Provides a framework for safeguarding against unauthorized access. Prevents attacks that compromise performance and availability.
Access data across any application with broad and flexible connectors, adaptors, and API services.
